BIOS Updates, a How-To Guide
HP BIOS (aka firmware) manages the hardware on every HP desktop, laptop, and workstation and receives several updates in a year. An HP BIOS update includes not only the basic firmware for the motherboard but may contain updates for individual hardware components that would not operate without their own firmware. When, let’s say, the USB-c controller gets updated by the manufacturer, Intel for example, a new version of the firmware may be packaged (along with the BIOS and other updates) into a single bin file residing in the BIOS Softpaq.
HP releases BIOS/Firmware updates 3-4 times/year for most platforms. These updates usually benefit users by patching vulnerabilities, fixing known issues, and providing important feature enhancements. With the rise of cyber virus and malware attacks, now also being attempted for the BIOS, keeping the BIOS updated is critical, and having an update process in place is becoming more important than ever.
NOTE: HP commercial BIOS firmware is cryptologically signed as part of HP’ BIOSPhere security. This can prevent most attacks where a BIOS update is attempted with a bogus bin file. These kinds of attacks have been increasing in cyberspace, and HP’s technology help prevent those attacks from succeeding.
HP provides several ways to update the BIOS on commercial platforms. This blog will review these options, including.
- Individual Web Download
- Via F10 Boot Setup menu
- Creating a BIOS Package for distribution
- Using the HP Client Management Script Library
- With HP Image Assistant
- Updating with WU
Individual Web Download
HP BIOS/Firmware updates are packaged into a Softpaq, and HP support web pages provide the latest information on BIOS and its download location.
The HP support site is hosted at Official HP® Support, where you can find the download pages for your device. As an example, here is a search for a HP ZBook 15 G5 Mobile Workstation

Once on location, selecting the ‘Software, Drivers and Firmware’ link will get to the listing that will include the latest BIOS Softpaq for the platform
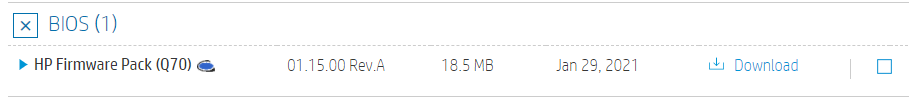
When downloading a BIOS softpaq and running the executable, you will be asked if you want to update the system or create media for installing on other, similar, devices. The
Softpaq will unpack (by default) to C:\SWsetup and open the dialog to choose your option
NOTE: HP Image Assistant (HPIA) is an great tool to find and download Softpaqs (including BIOS) for any supported platform and can be used to download and automatically unpack them. The setup can then be executed from the BIOS folder.

If you chose '(*) Update', the installation process will take the bin file (from the unpacked Softpaq location), split it into its various firmware components, and deposit each to the system UEFI partition. To note, the firmware bin file will contain the basic UEFI BIOS, but may also hold other required firmware updates, as mentioned above.
Once the pieces are in place on the UEFI system partition, the installation begins when the device reboots. During the reboot, the BIOS and all other components are installed. The update itself may reboot the device more than once, and for those systems with the HP Sure Start (BIOS self-healing) technology, the final reboot is where a backup copy of the system BIOS and security settings are stored in a secure HP Sure Start space. This backup copy of the BIOS is used to automatically recover should some kind of BIOS failure occur in the future.
NOTE: Due to the size of the firmware contained in the update, HP recommends a minimum system partition size of 300MB, and optimally 500MB to account for future needs.
F10 Setup
HP Commercial BIOS F10 Setup utility can be used to update the BIOS from either a local source (e.g., USB key) or HP.com, if network connectivity is available. For updating directly from HP, the default path that the BIOS will resolve to download the firmware file is preloaded and set up at the factory.


If the updated BIOS files have been posted to the system UEFI partition or a USB key (see section above for creating the USB key), the update is initiated.
Notice that this dialog shows additional settings to control BIOS updates. The F10 Setup Guide document describes these in detail
Creating a BIOS Package
Customers with Endpoint Management environments that would like to package BIOS updates to push to HP systems remotely, here are the steps to get it setup.
sp113769 /s /e

The CVA file is an initialization type of file that contains all the knowledge our tools use to handle the Softpaq, including the silent install instructions. For our purpose, opening sp113769.cva in Notepad, we see the following lines:

Using the HP Client Management Script Library (CMSL)
The HP Client Management script Library provides different methods to update the BIOS/Firmware on HP commercial systems. The CMSL commands are documented online at CMSL
If the update was allowed over the Internet, then a simple command like the following will do the trick and could be easily scripted. The first command confirms if there is an update to the installed version of the BIOS, and if Yes, then the BIOS is updated
if ( -not (Get-HPBiosUpdates –Check) ) {
Get-HPBiosUpdates –Flash [-Force] [[-Password] <String>] [-Bitlocker suspend]
}
The command will find the appropriate firmware Softpaq at HP, download it, and set up the UEFI partition. The [-Bitlocker] option can be used to suspend drive encryption so the next reboot will not require recovery action. The attractiveness of this command is that it has the intelligence to determine the correct BIOS to the system.
Updating BIOS from company source
For customers that want more control of the BIOS/Firmware update process or perhaps because Internet downloads are disallowed, the following CMSL method allows the BIOS/Firmware bin file to be used for the update. IT downloads the BIOS bin file for a required platform, create a package that runs a CMSL command with the bin file on each endpoint, send the command and bin file to each device needed the update.
The steps would then be
Download the BIOS bin file for a specific platform (next example for a HP ZBook 15 G5, motherboard ID/SysID: 842A). This command will download the latest version of the BIOS bin file
Get-HPBIOSUpdates -Platform 842A -Download -SaveAs <String> -Quiet
Next, create a package to copy the bin file to the device and run this command to update the BIOS. Password string can be included
Update-HPFirmware [[-Password] <String>] Q70_011600.bin
If the BIOS is password protected, the update command Update-HPFIrmware command will allow the password to be added as a runstring option, as shown above.
The CMSL modules Softpaq and can be unpacked and installed on ALL supported HP commercial systems (supported product list is the same as for HP Image Assistant). An easy installation option is to copy the folder of the unpacked CMSL Softpaq to each client at:
%ProgramFiles%\WindowsPowerShell\Modules
Then, a script can simply import the modules with
Import-module HPCMSL
and use any of the available commands
HP Image Assistant (HPIA)
HP Image Assistant (HPIA) can perform BIOS updates by itself and be scripted to silently run on a supported HP client device. Here is the list of supported patforms. IT Administrators can package HPIA to run directly on each client from a local path, or a remote share. HPIA does not require installation so it will execute directly from the folder it run from.
The following command will update the BIOS (and ONLY the BIOS) of the system it is running on – but only if required !!!:
cd ..\HPIA_Path .\HPImageAssistant.exe /Operation:Analyze /Category:BIOS /action:Install /silent /reportFolder:c:\HPIA\Report /Debug
The /Debug option is not required, but always useful as it generates an additional detail log with much more information that can be useful for troubleshooting installation issues.
HP Image Assistant can also pull BIOS update files from a company share folder (acting as a repository). When HPIA command includes the runstring option ‘/Offlinemode:<path_to_repo>’, it will reach out to the path listed instead of contacting HP. Details on creating and maintaining an HPIA repository folder is described in this blog
NOTE: If the HP CMSL is installed on a client device, you can use a CMSL command to download and install (e.g., unpack it to a folder of your choosing), and be available for use.
import-module hpcmsl Install-HPImageAssistant -Extract [[-DestinationPath] <String>]
Updating via WU
At the time a BIOS update is packaged into an HP Softpaq and posted on HP's FTP, the contents of the Softpaq (not the Softpaq itself) is uploaded to Microsoft's Windows Update database. Windows Update then can make the BIOS firmware available to devices that are scanning against it. Note that Microsoft has built telemetry into the process that might hide certain updates, including BIOS/firmware, if the telemetry shows that a number of failures were encountered
For devices with Windows 10 Pro, WU will scan on its regular schedule and if a BIOS update was available in the backend it will be offered and applied. For Enterprises that are managing updates via Windows Update for Business, you have to enable these updates to apply via WU on end user devices